Math2.org Math Tables: Expansions for PI
|
| (Math) |

PI = 3. 1415926535 8979323846 2643383279 5028841971 6939937510 5820974944 5923078164 0628620899 8628034825 3421170679 ...
Vieta's Formula
![\[\frac{2}{\pi} =
\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}
\frac{\sqrt{2 + \sqrt{2}}}{2}
\frac{\sqrt{2 + \sqrt{2 + \sqrt{2}}}}{2}
...
\] \[\frac{2}{\pi} =
\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}
\frac{\sqrt{2 + \sqrt{2}}}{2}
\frac{\sqrt{2 + \sqrt{2 + \sqrt{2}}}}{2}
...
\]](/math/tex/641f6fb3fd4b5a0a5d70eda0420897d0.png)
Leibnitz's Formula
PI/4 = 1/1 - 1/3 + 1/5 - 1/7 + ...
Wallis Product
PI/2 = 2/1 * 2/3 * 4/3 * 4/5 * 6/5 * 6/7 * ...2/PI = (1 - 1/22)(1 - 1/42)(1 - 1/62)...
Lord Brouncker's Formula
4/PI = 1 + 1
----------------
2 + 32
------------
2 + 52
---------
2 + 72 ...
(PI2)/8 = 1/12 + 1/32 + 1/52 + ...
(PI2)/24 = 1/22 + 1/42 + 1/62 + ...
Euler's Formula
(or more generally...)
B(k) = the k th Bernoulli number.
eg. B0=1 B1=-1/2 B2=1/6 B4=-1/30 B6=1/42 B8=-1/30 B10=5/66.
Further Bernoulli numbers are defined as
(n 0)B0 + (n 1)B1 + (n 2)B2 + ... + (n (n-1))B(N-1) = 0
assuming all odd Bernoulli #'s > 1 are = 0.
(n k) = binomial coefficient = n!/(k!(n-k)!)
See Power Summations #2 for simplified expressions (without the Bernoulli notation) of these sums for given values of k.
(PI2)/6 =
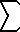 (n = 1..
(n = 1..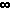 ) 1/n2 = 1/12 + 1/22 + 1/32 + ...
) 1/n2 = 1/12 + 1/22 + 1/32 + ...
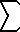 (n = 1..
(n = 1..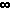 ) 1/n(2k) = (-1)(k-1) PI(2k) 2(2k) B(2k) / ( 2(2k)!)
) 1/n(2k) = (-1)(k-1) PI(2k) 2(2k) B(2k) / ( 2(2k)!)
